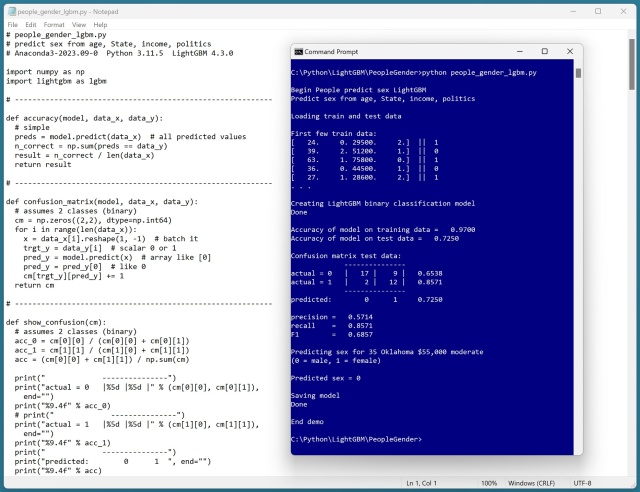
LightGBM, a powerful tree-based system, offers binary and multi-class classification, regression, and ranking. Python's user-friendly API makes it easy to install and use LightGBM for model evaluation, despite the challenge of managing numerous parameters.
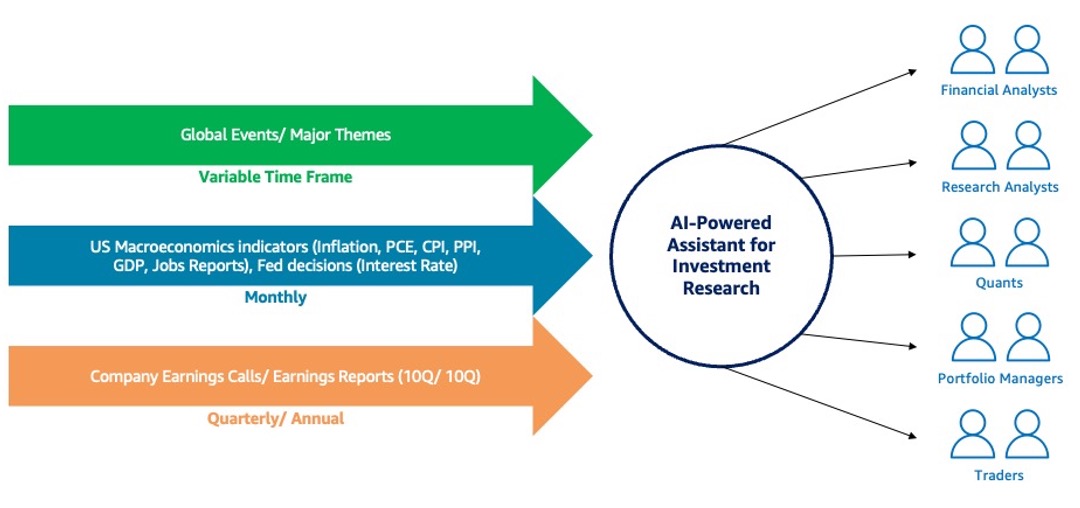
AI-powered assistants using Generative AI and large language models (LLMs) are transforming investment research in capital markets by automating tasks and boosting productivity for financial analysts. These assistants can gather and analyze multifaceted financial data from various sources, enabling analysts to work faster and more accurately in making investment decisions.
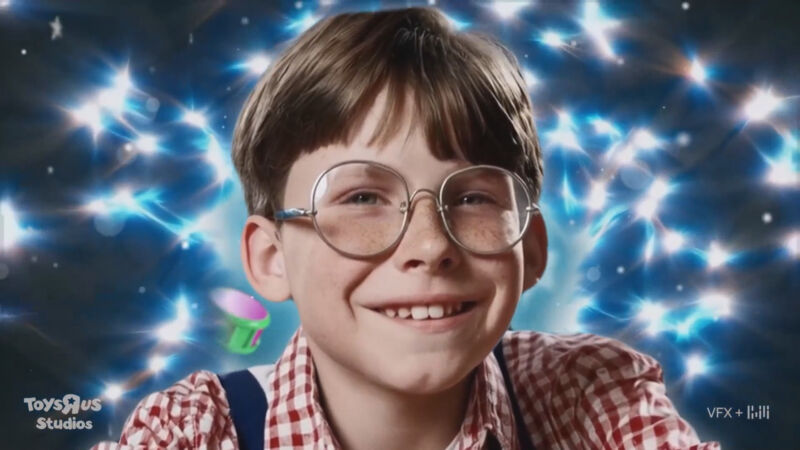
Toys "R" Us partners with Native Foreign to create brand film using OpenAI's Sora text-to-video tool, showcasing founder's story. Sora generates AI video clips of realistic scenes and characters from text instructions, pushing boundaries of technology in commercial production.
Bill Gates believes AI will boost efficiency for tech and grids, outweighing datacentres' energy use. AI to aid climate goals, not hinder them, by reducing energy consumption.
NBC plans to use AI-generated clone of Al Michaels' voice for daily Olympic recaps, sparking concerns about future sports commentators. Michaels, known for iconic calls since 1971, will narrate 2024 Summer Olympics on Peacock, despite being dropped from NFL coverage in 2023.
Article presents Nearest Centroid Classification for Numeric Data in Microsoft Visual Studio Magazine. Nearest centroid classification is easy, interpretable, but less powerful than other techniques, achieving high accuracy in predicting penguin species.
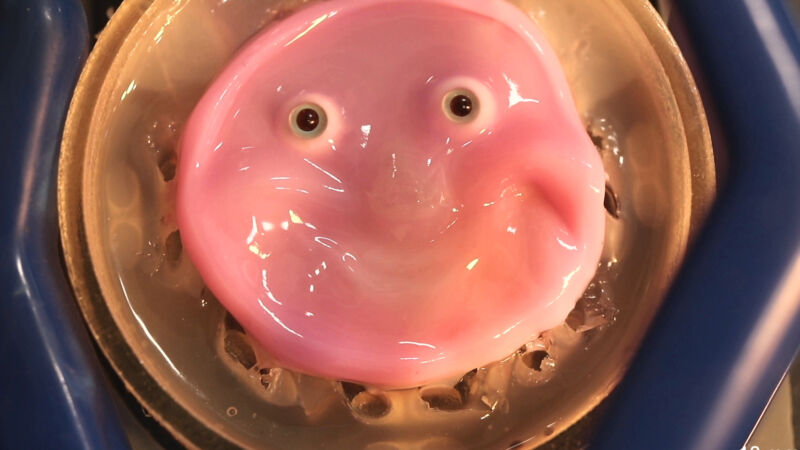
Researchers from University of Tokyo and Harvard create lifelike robotic skin with human cells, capable of conveying emotions. The study explores benefits of using living tissue for robot covering, emphasizing potential for self-repair.
Optimal workload distribution in microservice applications is crucial for handling thousands of requests per second. Load balancers and health checks play key roles in distributing requests and maintaining system efficiency.
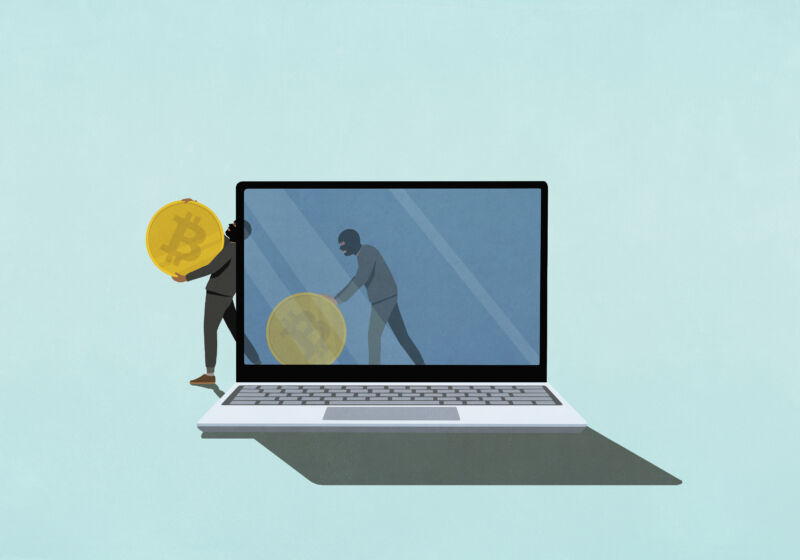
24-year-old Remy Ra St. Felix led a violent gang targeting cryptocurrency savings, committing armed robberies, assaults, and even a kidnapping. Despite only stealing $150,000 in crypto, the gang inflicted harm on 11 victims across four US states, highlighting the dangers of physical crypto theft.
Centre for Long-Term Resilience urges UK government to track AI incidents to prevent risks. CLTR recommends central hub for logging AI-related episodes nationwide.
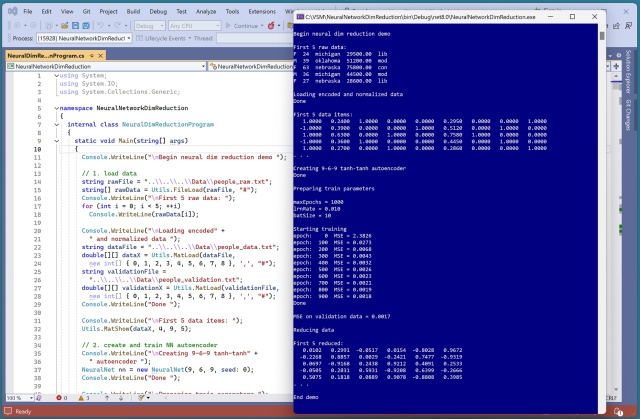
Dimensionality reduction using PCA & neural autoencoder in C#. Autoencoder reduces mixed data, PCA only numeric. Autoencoder useful for data visualization, ML, data cleaning, anomaly detection.
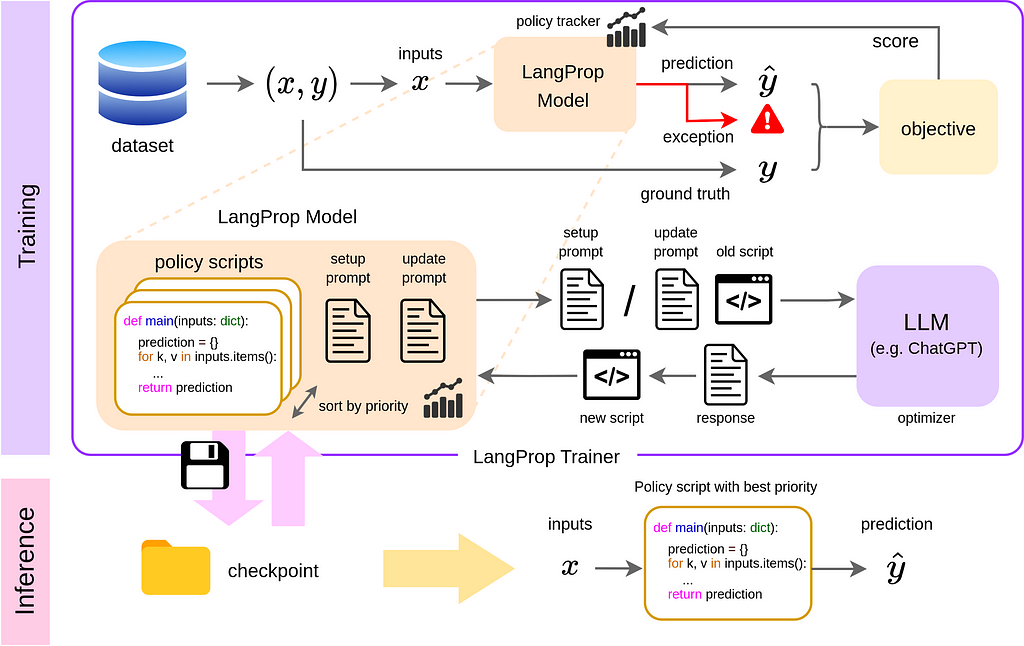
ChatGPT powers autonomous driving research at Wayve using LangProp framework for code optimization without fine-tuning neural networks. LangProp presented at ICLR workshop showcases LLM's potential to enhance driving through code generation and improvement.
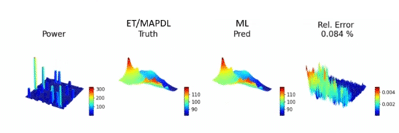
Ansys utilizes NVIDIA technology to tackle complex challenges in 3D-IC design at the Design Automation Conference. Using NVIDIA Omniverse and Modulus, Ansys engineers can optimize chip performance and reliability with AI-based surrogate models for faster simulations.
Researchers from UC Santa Cruz, UC Davis, LuxiTech, and Soochow University have developed an AI language model without matrix multiplication, potentially reducing environmental impact and operational costs of AI systems. Nvidia's dominance in data center GPUs, used in AI systems like ChatGPT and Google Gemini, may be challenged by this new approach using custom-programmed FPGA chips.
Large language models (LLMs) enable human-like conversations but can also spread misinformation and harmful content. Guardrails are crucial for mitigating risks in LLM applications, ensuring safe and desirable outputs.