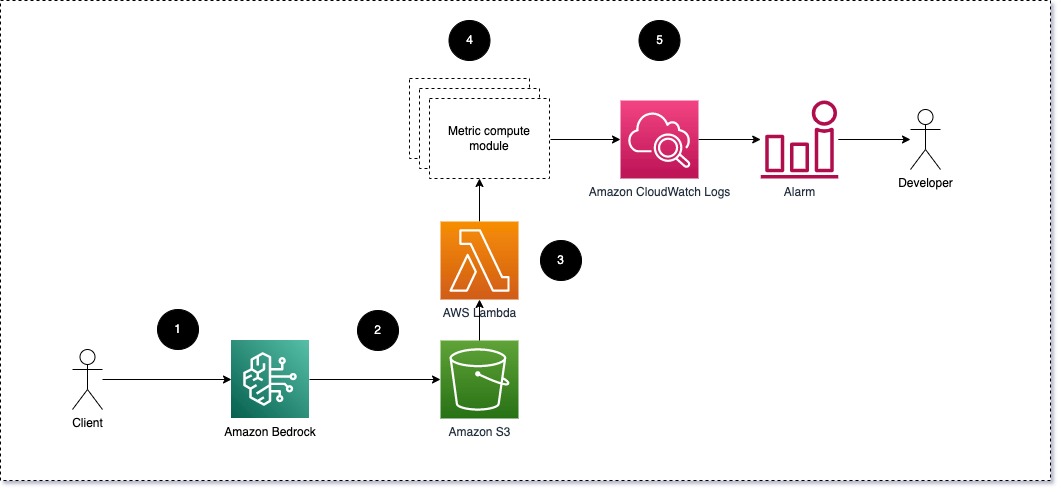
LLMs have transformed NLP tasks, but monitoring their performance is crucial. Our scalable AWS architecture offers real-time visibility and customizable solutions for online LLM monitoring, including tracking semantic similarity metrics with embeddings.
New NVIDIA RTX 500 and 1000 Ada Generation Laptop GPUs offer powerful AI acceleration for professionals on the go, boosting productivity and efficiency across industries. Enhanced with NPU and RTX GPU, these GPUs deliver up to 14x generative AI performance, 3x faster photo editing, and 10x graphics performance compared to CPU-only configurations.
MIT Media Lab students created Pienso to detect cyberbullying, misinformation, and more without coding. White House demo led to empowering domain experts for AI success.
MIT's LIDS receives $1.36M ARC grant for AI-driven smart grid modeling project. Collaboration with universities and startups to revolutionize energy sector with generative AI models and HILLTOP+ platform.
MIT researchers developed a deep-learning model to decongest robotic warehouses, improving efficiency by nearly four times. Their innovative approach could revolutionize complex planning tasks beyond warehouse operations.
Exciting developments in Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized communication, prompting is key to harnessing their in-context learning abilities. Companies like Prompting Llama and GPT-3.5 are leading the way in innovative prompting strategies for LLMs.
Explore the complex yet effective Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) approach for fast nearest neighbour search. Journey through the history and intricacies of HNSW to understand its high-speed, high-recall capabilities.
Machine learning pitfalls: overfitting, misleading data, hidden variables. Examples include failed Covid prediction models and water quality system. REFORMS checklist introduced to prevent errors in ML-based science.
Learn what not to do with statistics in this intriguing report by Banks and Boothroyd. Discover how spurious correlations can mislead and the dangers of p-hacking.
Article highlights deploying ML models in the cloud, combining CS and DS fields, and overcoming memory limitations in model deployment. Key technologies include Detectron2, Django, Docker, Celery, Heroku, and AWS S3.
The Direct Preference Optimization paper introduces a new way to fine-tune foundation models, leading to impressive performance gains with fewer parameters. The method replaces the need for a separate reward model, revolutionizing the way LLMs are optimized.
Filmmaker Tyler Perry halts $800 million studio expansion due to AI video generator Sora's capabilities. OpenAI's Sora stuns with text-to-video synthesis, surpassing other AI models.
AI models like STEFANN, SRNet, TextDiffuser, and AnyText are revolutionizing Scene Text Editing, making it easier to modify text in images while preserving aesthetics. Companies like Alibaba and Baidu are actively researching and implementing STE for practical applications like enhancing text recognition systems.
Article highlights: 'Matrix Inverse from Scratch Using SVD Decomposition with C# in Microsoft Visual Studio Magazine. Importance in machine learning, SVD algorithm implementation in C# for matrix inverse.'
Stability AI unveils Stable Diffusion 3, a cutting-edge image-synthesis model promising enhanced quality and accuracy in text generation. The open-weights model family ranges from 800 million to 8 billion parameters, allowing for local deployment on various devices and challenging proprietary models like OpenAI's DALL-E 3.