Researchers have joined forces to create a programmable quantum processor that operates with high fault tolerance based on logical qubits. This opens up new prospects for large-scale and reliable quantum computing, capable of solving previously intractable problems.
The Turing test, once groundbreaking for machine thinking, is now limited by AI's ability to mimic human reactions. A new study introduces a three-step system to determine whether artificial intelligence can reason like a human.
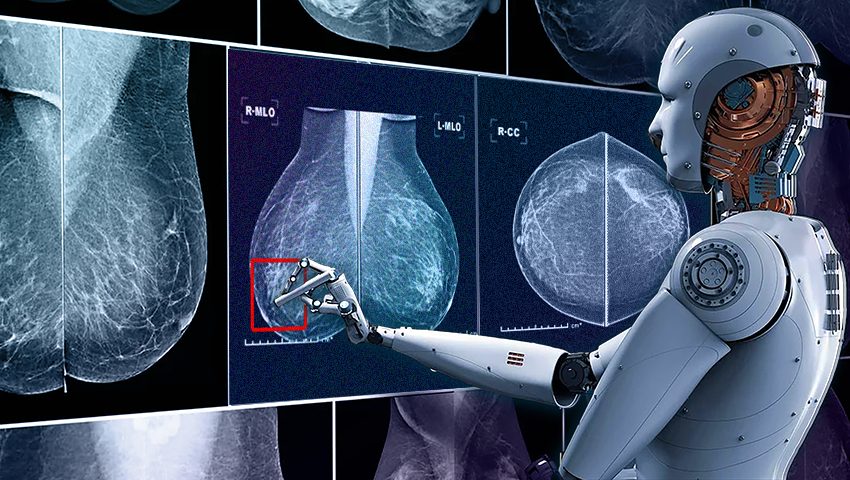
QuData introduces an innovative AI-powered breast cancer diagnostic system. This transformative technology ensures early detection and prompt intervention, marking a significant step forward in accessible, accurate, and timely treatment with better outcomes.
A groundbreaking NLP model Gemini AI is set to surpass existing benchmarks. With its multimodal prowess, scalability across various domains, and integration potential within Google's ecosystem, Gemini AI represents a significant leap in AI technology.
ALERTA-Net is a new deep neural network that combines social networks, macroeconomic indicators and search engine data. The unique model predicts stock price movements and stock market volatility, going beyond traditional analysis methods.
In 1950, British scientist Alan Turing proposed a test to determine whether machines can think. To date, no artificial intelligence has yet successfully passed it. Will ChatGPT be the first?
Lincoln Laboratory is actively advancing efforts to diminish the energy consumption of AI models. Their objectives encompass fostering transparency in energy usage and enhancing the efficiency of AI model training.
OpenAI had an impressive DevDay introducing new features. Let's dive into the world of innovation and explore new horizons in the landscape of artificial intelligence. Find out about all the new amazing possibilities in our article!
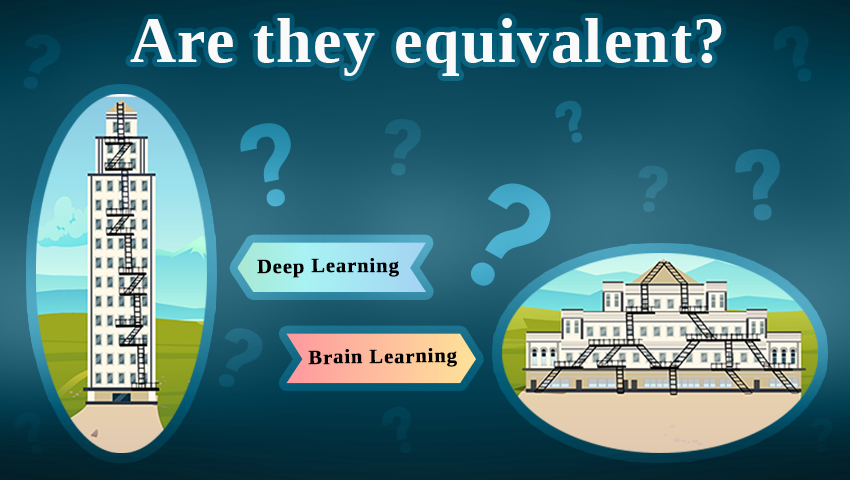
Continuing research on tree-like architectures, scientists from Bar-Ilan University examine the need for deep learning in AI and suggest alternative machine learning methods that may be more effective for complex classification tasks.
Researchers from the Institute for Assured Autonomy highlight new methods for ensuring safety in the growing world of unmanned aircraft systems using advanced artificial intelligence techniques and simulation environments.
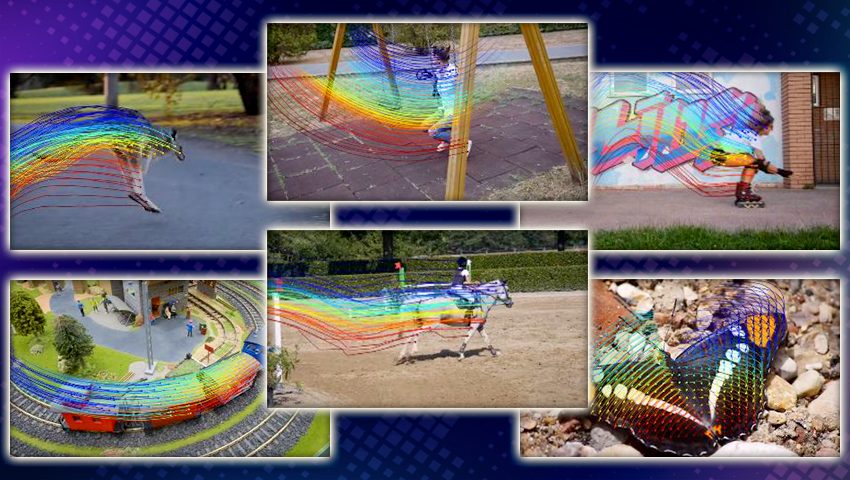
The latest motion estimation method can extract long-term motion trajectories for every pixel in a frame, even in the case of fast movements and complex scenes. Learn more about the exciting technology and the future of motion analysis in this article about OmniMotion.
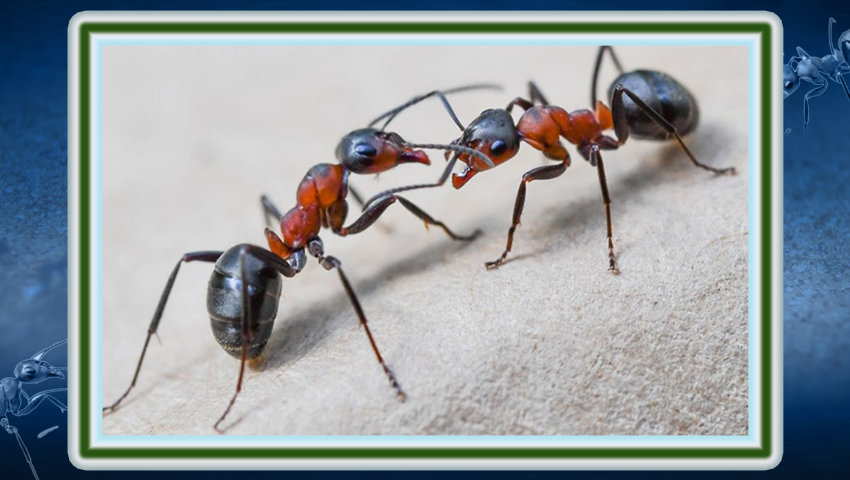
Inspired by ants, researchers from the Universities of Edinburgh and Sheffield are developing an artificial neural network to help robots recognize and remember routes in complex natural environments.
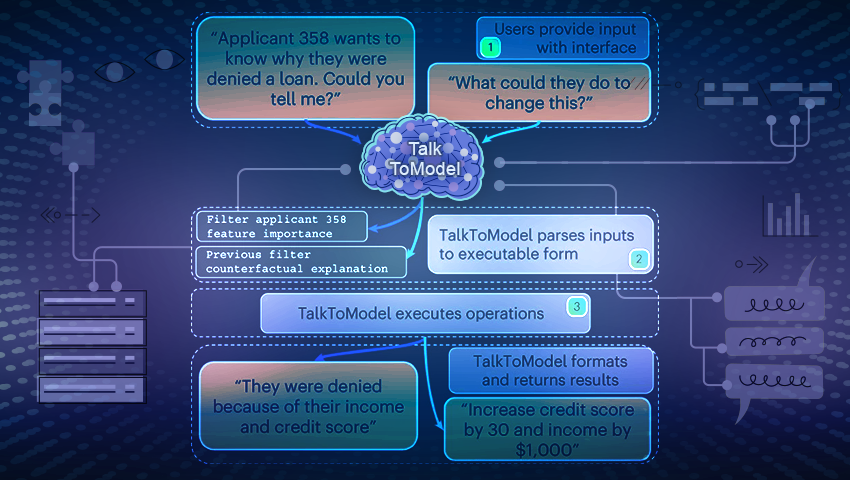
TalkToModel is an innovative system for enabling open conversations with ML models. This platform allows users to not only understand, but also communicate with ML models in natural language, as well as receive explanations of their predictions and operating processes.
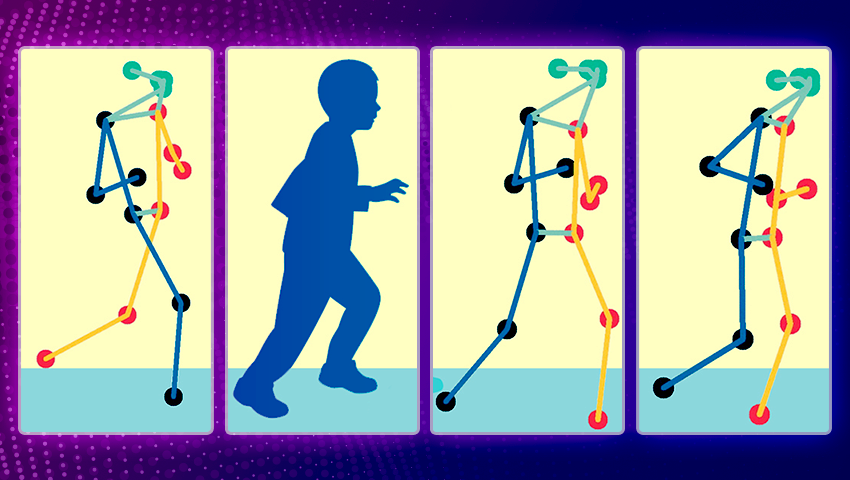
The new technique utilizes real-time video analysis to compute a clinical score of motor function based on specific pose patterns, reducing the need for frequent in-person evaluations and enhancing patient care.
Recent AI research centered around tree-based architectures opens new perspectives for training artificial neural networks.