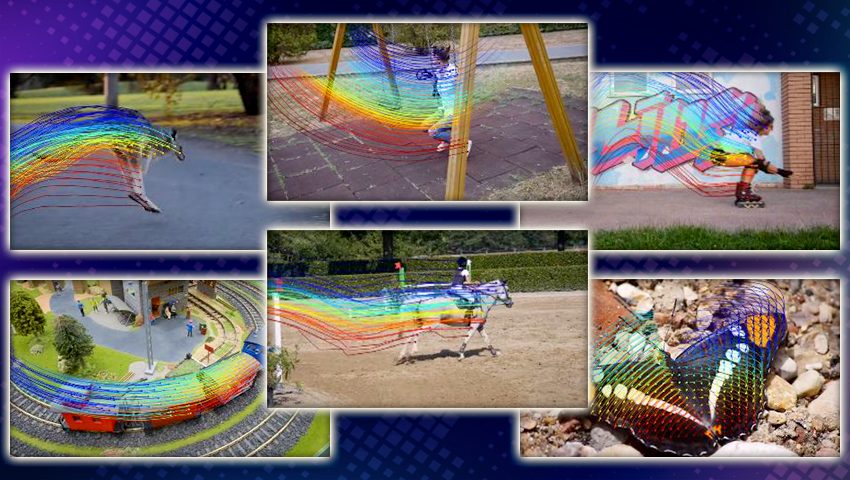
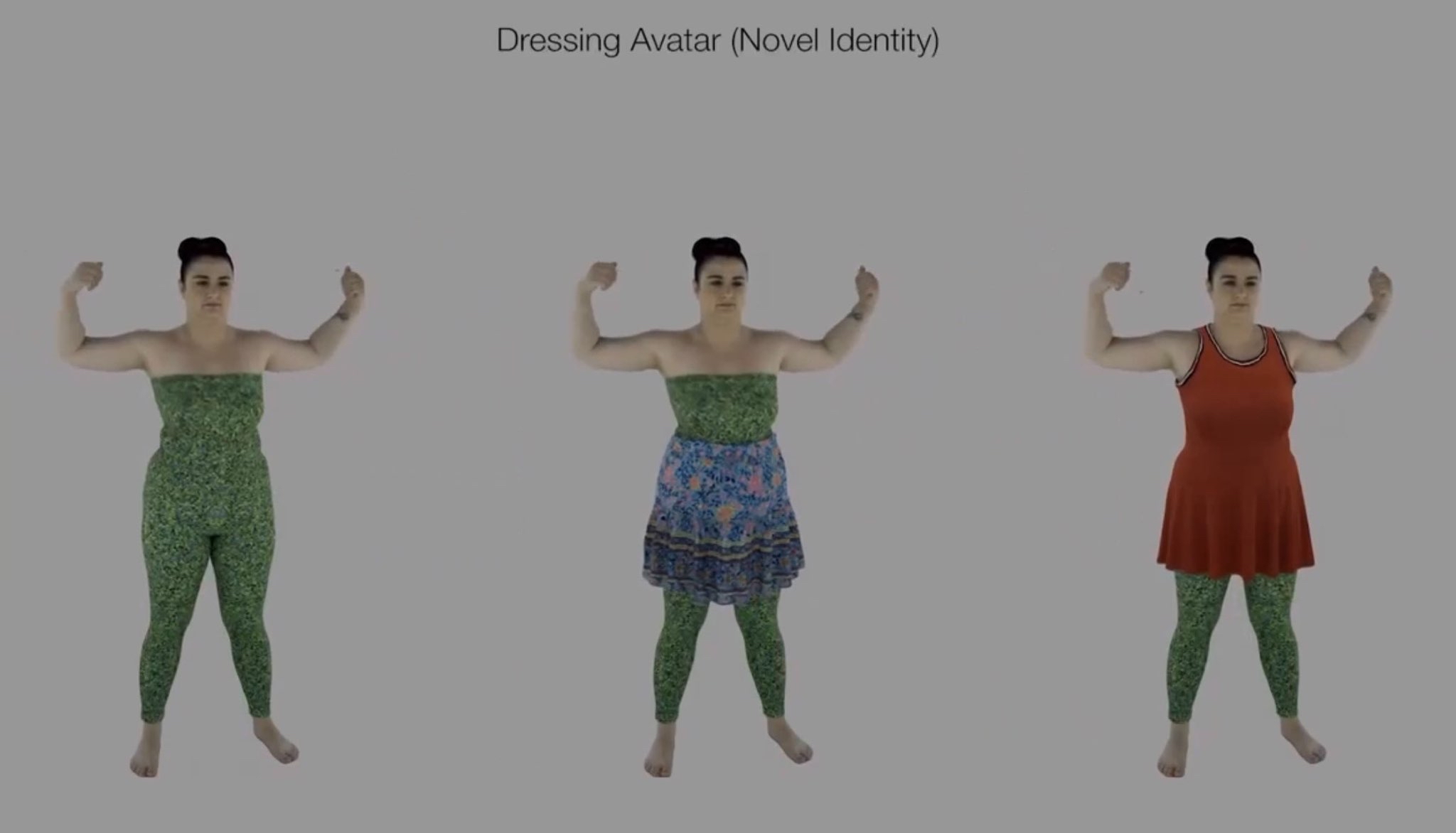
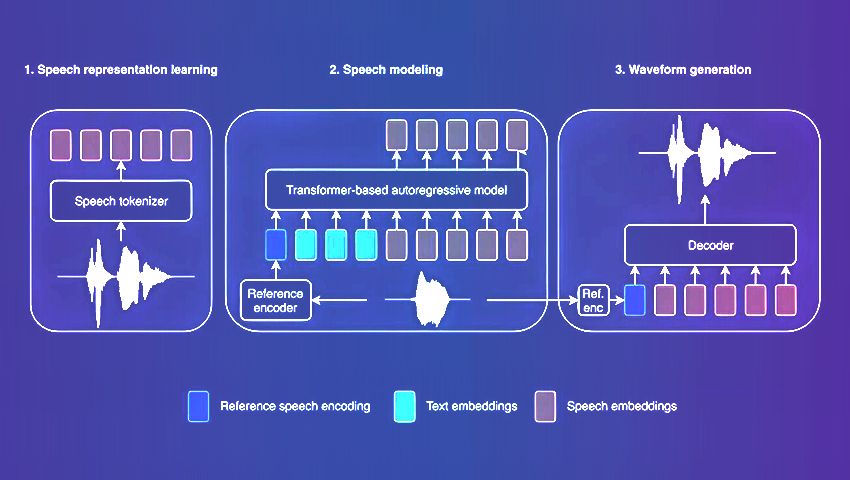
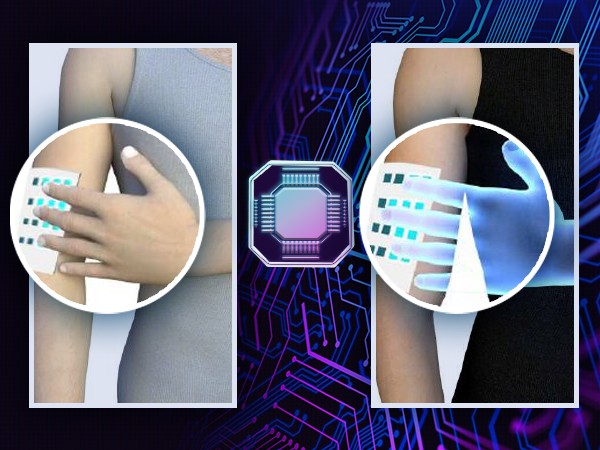
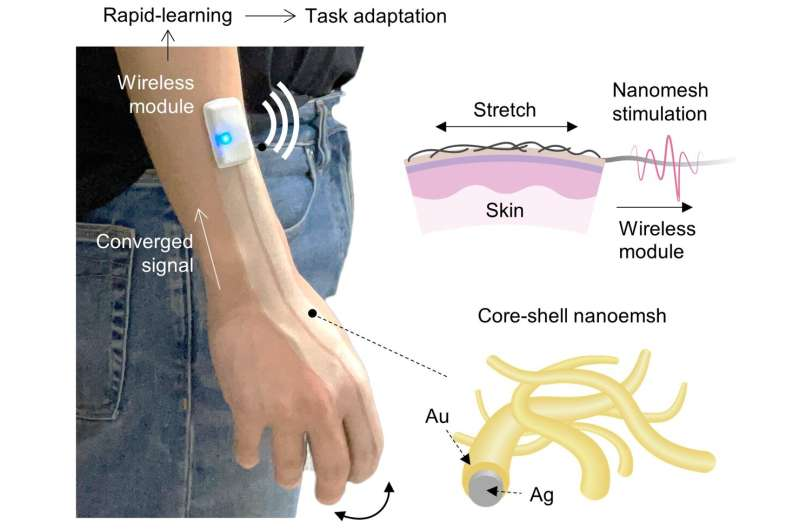
Researchers have discovered a simple mathematical way to “steer” AI models by directly manipulating internal concept vectors – improving performance while revealing hidden risks. Now AI behavior can be controlled more precisely than ever, but also raises concerns about how easily safeguards can be bypassed.
OpenAI and Anthropic are redefining the capabilities of AI, introducing models that tackle complex tasks from coding to multi-step knowledge work. With features like agentic collaboration, long-context reasoning, and autonomous problem-solving, these upgrades showcase AI’s potential as an intelligent digital collaborator across professional workflows.
Moltbook is a social network where autonomous AI agents interact, form communities, and generate content, offering a rare glimpse into machine-to-machine social behavior at scale. While fascinating, the experiment has already raised serious security and governance concerns due to agents’ access to sensitive data and real-world systems.
OpenAI has shared new insights into how its AI coding assistant Codex works, revealing how it combines powerful language models with automated tools to write, test, and modify code. The explanation highlights both the growing power of AI in software development and the careful design needed to keep these systems fast, safe, and reliable.
China is unleashing its AI Tigers on the world stage, as Zhipu AI and MiniMax make their landmark debut on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. With one building the country’s technological backbone and the other creating consumer-ready AI for global audiences, their rise signals that the next chapter of AI will be fiercely competitive.
Anthropic’s Cowork marks a major shift from chat-based AI to autonomous digital coworkers that can plan and execute real work directly on your computer. By giving the controlled access to local files, Cowork becomes a practical collaborator for reports, analysis, and file management.
In 2026, AI moves beyond chatbots to become the operating layer of modern enterprises and creative industries. Our prognosis explores the key shifts shaping the year ahead: from “digital coworkers” and multimodal intelligence to MCP as the backbone of scalable AI.
In 2025, AI moved from hype to reality, becoming a core force shaping how we create content, browse the web, work, and make decisions. This article explores the biggest shifts: the rise of agentic AI and vibe coding, tightening regulation, and the growing battle over quality and trust.
NVIDIA’s Nemotron 3 is a new family of open AI models built for efficient, large-scale multi-agent systems, offering up to a 1-million-token context window. Powered by a hybrid Mamba-Transformer MoE architecture, it delivers high inference throughput while enabling transparent, scalable, and cost-effective AI agents for real-world use.
The Speech-to-Reality system transforms spoken commands into physical objects using a combination of natural language processing, 3D generative AI, and robotic assembly. The system enables users to request items like chairs, stools, or shelves and have them assembled by a robotic arm in as little as five minutes.
Scientists have engineered a transneuron – an artificial neuron capable of mimicking the activity of multiple regions of the human brain. This advancement could accelerate the development of robots with human-like perception, adaptability, and learning.
Google has launched Gemini 3, its most advanced AI model yet, along with Antigravity, a new agent-first platform that lets AI autonomously plan and execute complex tasks. Together, they elevate learning, coding, and workflow automation with enhanced reasoning and multimodal capabilities.
Recent research has revealed that AI language models store memory and reasoning in entirely separate neural circuits, showing that machines “think” and “remember” in different ways. This discovery leads the way to creating AI systems that can forget sensitive data while preserving their intelligence.
For the first time ever, a quantum computer has beaten the world’s fastest supercomputer! Google researchers announced Quantum Echoes, a breakthrough algorithm that runs on their new Willow quantum chip.
Mamba-3 - state-space model that redefines how AI thinks, learns, and understands language. By improving context tracking, information processing, and response generation, Mamba-3 sets a new standard for performance and inference speed, beyond traditional transformer models.
Researchers at UCLA have developed optical generative models – AI technology that creates images using light instead of traditional electronic computation. This innovation delivers high-speed, energy-efficient image generation with quality comparable to digital diffusion models.
Google DeepMind has introduced Gemini Robotics – an AI system that allows robots to “think before acting,” plan complex tasks, and even transfer skills across different robot types. With advanced reasoning, safety features, and cross-embodiment learning, robots become truly intelligent.
Now AI can autonomously generate the “brains” of robots, creating a fully functional drone control system 20 times faster than humans. The experiment with generative AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude reveals both the potential and current limits of machines building machines.
NASA and IBM have created Surya, a powerful AI model that can predict solar flares and space weather. By providing early warnings, it helps safeguard satellites, power grids, and renewable energy systems from damaging solar storms – a perfect example of how AI helps protect technology and drive green innovation.
Anthropic’s new Threat Intelligence Report uncovers how AI is being twisted for cybercrime, fueling schemes from extortion to global fraud. The findings reveal a dark side of AI, where powerful tools once meant to help are now being exploited in ways that raise urgent security concerns.
Meta AI’s DINOv3 is a self-supervised vision model trained on 1.7 billion images, setting new standards in image classification, object detection, and beyond. With innovations like Gram anchoring and real-world impact from monitoring deforestation to powering NASA’s Mars exploration, it marks a paradigm shift in computer vision.
The new system enables groups of robots to act as a unified team. The MultiRobot FrameWork lets robots share real-time information about their environment, positions, and tasks, mirroring the collective behavior seen in insect colonies, but powered by advanced sensors and computation.
The new GenSeg framework significantly reduces the need for expert-labeled data and achieves high-accuracy medical image segmentation with as few as 40-50 samples. By creating realistic synthetic scans paired with exact labels, it empowers the development of advanced diagnostic tools even in data-limited settings.
OpenAI's newest open-weight models gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b bring advanced reasoning and 128K-token context windows – all under Apache 2.0 license. With support for local deployment and optimization for consumer hardware, these models mark a major shift toward transparent and decentralized AI.
Skydweller is a solar-powered drone designed for long-endurance missions. With AI-powered radar, self-healing systems, and the ability to fly autonomously for up to 90 days straight, it sets a new standard for persistent aerial surveillance and data collection.
New research reveals that LLMs like GPT-4o and Gemma 3 often stick to their initial answers even when wrong – yet quickly lose confidence when challenged. This surprising mix of overconfidence and self-doubt mirrors human cognitive biases and raises concerns about AI reliability.
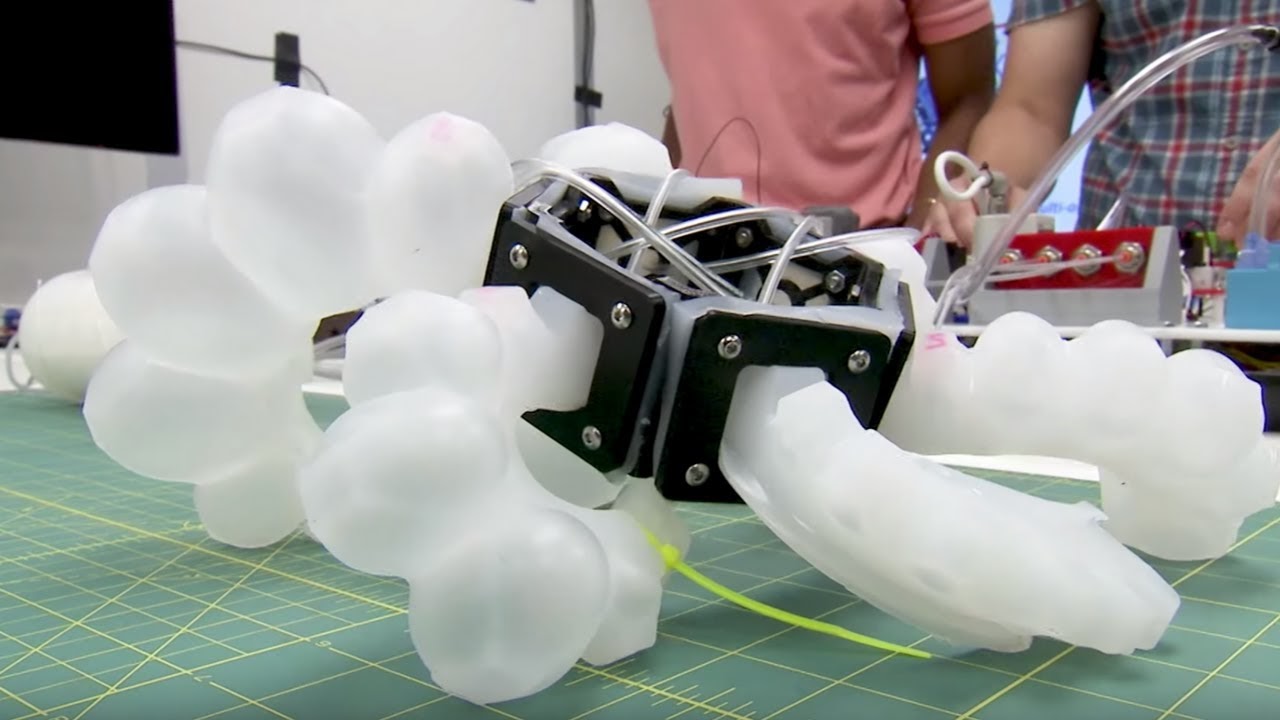
Traditional rigid robots are incapable of a wide range of tasks. Instead soft robots may interact with people more safely or easily access narrow spaces. However, for robots to successfully complete their goal, it is essential to know the exact position of their body parts. That’s a complex task for a soft-bodied robot that can undergo nearly infinite number of modifications.
MIT scientists explored a critical flaw in AI language models called position bias, where models favor information at the beginning and end of text while ignoring the middle. Their research reveals this bias is rooted not only in the training data, but also in the architecture of the models themselves.
A self-powered artificial synapse can mimic human color vision with 10-nanometer resolution using dye-sensitized solar cells. This technology enables energy-efficient AI systems capable of advanced color recognition and logic processing.
MIT researchers have developed CAV-MAE Sync, an AI model that learns to precisely link sounds with matching visuals in video without any labels. This technology can bring us closer to smarter AI that can see, hear, and understand the world just like humans.
The most fascinating innovations presented at Google I/O 2025 reveal how AI is transforming Search, video creation, and communication. These advances are redefining everyday technology, making it smarter, more intuitive and personalized than ever before.
The most advanced AI models from tech giants like OpenAI and DeepSeek are generating false information at unprecedented rates – and no one knows exactly why. Due to this surge in AI “hallucinations”, the reliability of AI across critical fields is being called into question.
Microsoft’s Phi-4 family is a new generation of compact language models built for complex tasks like math, coding, and planning – often outperforming larger systems. Trained with advanced techniques and curated data, they offer strong reasoning while staying efficient for low-latency use.
Why stress over every line of code when AI can "vibe" its way through development for you? Vibe coding is a fast-growing trend where developers let AI take the lead in writing code, transforming programming into a more intuitive and spontaneous process.
NVIDIA has officially made its PhysX engine and Flow SDK fully open source, including the long-awaited GPU simulation kernel code, under the permissive BSD-3 license. Now developers can customize, port, and revive advanced physics simulations across platforms – even on non-NVIDIA GPUs.
Midjourney has launched V7, its most powerful AI image model yet, featuring smarter prompts and real-time personalization. With a redesigned architecture, V7 delivers improved object coherence, enhanced texture realism, and introduces Draft Mode for rapid, cost-efficient image iteration.
A new advanced neural system that mimics the brain’s learning processes promises to create faster, more efficient, and energy-saving AI. By leveraging Hebbian learning and spike-timing-dependent plasticity, this innovation could enhance AI performance while significantly reducing environmental and economic costs.
ItpCtrl-AI improves X-ray diagnostics by mimicking radiologists' gaze patterns, providing interpretable heatmaps that enhance transparency and trust in AI-driven medical imaging. By filtering out irrelevant data and focusing on key diagnostic areas, the system ensures more accurate and explainable results.
GPT-4.5, OpenAI's most advanced AI yet, features improved natural language understanding, enhanced emotional intelligence, and more intuitive conversations. It excels in writing, brainstorming, and problem-solving while minimizing AI hallucinations for more reliable results.
MIT researchers have developed MiFly, a low-power, RF-based system that enables drones to self-localize in complete darkness, indoors, and in low-visibility conditions. By using a single backscatter tag and dual-polarization radar, MiFly navigates without relying on visual cues or external infrastructure.
NVIDIA Cosmos enhances AI robotics by generating photorealistic 3D environments, allowing developers to train autonomous systems without relying on costly real-world data. With advanced world foundation models, Cosmos drives innovation in robotics, self-driving cars, and industrial automation.
HunyuanVideo is the largest open-source AI model for video generation, boasting 13 billion parameters to produce high-quality, cinematic videos with lifelike motion and perfectly synchronized audio. Setting a new benchmark for AI-driven content creation, it delivers unmatched realism, precision, and creative possibilities.
The two-trajectory planning system lets MAVs explore unknown paths while always maintaining a safe backup route. Powered by LiDAR-based perception and the CIRI algorithm, drones dynamically generate real-time flight paths for high-speed navigation in unpredictable environments.
Edify 3D by NVIDIA creates high-quality 3D models in under 2 minutes using AI. By combining multi-view diffusion models and Transformers, it offers fast, accurate, and scalable 3D generation from text or images, making it a perfect solution for gaming, animation, and design industries.
Microsoft has launched the Phi-4 model with open weights under the MIT license, offering researchers and developers unprecedented flexibility. With 14 billion parameters, Phi-4 outperforms its counterparts in solving mathematical problems and multitasking, ensuring efficient work with limited resources.
RadiologyLlama-70B is an advanced AI model trained on over 6.5 million medical reports to enhance the analysis of radiological findings. The model can significantly improve radiologists' workflows, delivering remarkable accuracy while reducing computational costs.
Alibaba's new AI model, QwQ-32B-Preview, challenges ChatGPT with its impressive math and logic skills, outperforming competitors on key benchmarks. Released under an open license, it offers advanced reasoning capabilities but still struggles with tasks requiring strong common-sense understanding.
Anthropic has introduced the Model Context Protocol – an open-source framework that simplifies AI integration with data sources and external tools. By providing a universal standard, MCP enhances AI capabilities and eliminates the need for custom solutions.
Anthropic has introduced Claude 3.5 Sonnet, a new AI model capable of controlling a computer similarly to a human. The model uses screenshots of the desktop to navigate applications and perform tasks such as clicking, typing, and gathering information.
Stable Diffusion 3.5, the latest release from Stability AI, introduces three powerful model variants that deliver enhanced image quality, speed, and accessibility for consumer hardware. The models are free for non-commercial use, and integrate advanced safety features to prevent misuse.
The 2024 Nobel Prizes in physics and chemistry have set a precedent for acknowledging AI’s contributions to science. While some may question the fit between AI and traditional disciplines, others see this as a necessary step toward recognizing the interdisciplinary nature of modern research.
Meta has unveiled Movie Gen, an AI-powered tool that creates high-definition videos with synchronized sound from simple text prompts. The model provides advanced video creation and editing features, offering users enhanced control over content generation.
With price cuts, increased rate limits, and faster output, new Gemini models by Google make advanced AI more accessible for developers worldwide. They boost speed, reduce costs, and enhance performance across a wide range of text, code, and multimodal tasks.
OpenAI o1 is designed to excel in complex reasoning tasks across science, coding, and mathematics. The new model aims to improve accuracy by mimicking human-like reasoning and address safety concerns, ensuring more reliable and responsible AI usage.
Developed by researchers from Boston University, Neural Phase Retrieval leverages deep learning techniques to enhance the reconstruction of high-resolution images from low-resolution data. New neural framework NeuPh is already successfully outperforming traditional methods.
The Indian Patent Office has granted a patent for the innovative landing system for mini-UAVs. This technology enables precise landings in challenging terrains and has potential applications in both military and civilian logistics, including high-altitude deliveries and emergency.
The latest text-to-image model from Ideogram AI introduces significant advancements that could challenge the dominance of established players like MidJourney and Leonardo AI. New features are already available, including multiple distinct styles, enhanced realism, and advanced prompting tools.
A low-cost, innovative accident avoidance system for drones uses onboard sensors and cameras to autonomously prevent mid-air collisions. This technology is crucial for UAV operations, ensuring safety and efficiency in increasingly crowded airspaces.
A new computer vision system significantly reduces energy consumption while providing real-time, realistic spatial awareness. It enhances AI systems' ability to accurately perceive 3D space – crucial for technologies like self-driving cars and UAVs.
Gen-3 Alpha – new AI model introduces powerful tools for generating high-quality videos, offering creatives unprecedented control and realism. With its advanced features and superior quality, the model pushes the boundaries of AI-driven content creation, outpacing competitors.
MAIA can interpret neural networks by conducting experiments and refining its analysis, enhancing understanding of AI models. This agent can identify neuron activities, remove irrelevant features, and detect biases, making AI systems safer and more transparent.
Researchers created insect-inspired autonomous navigation strategies for tiny, lightweight robots. Tested on a 56-gram drone, the system enables it to return home after long journeys using minimal computation and memory.
Drone racing has been used to test neural networks for future space missions. This project aims to autonomously manage complex spacecraft maneuvers, optimizing onboard operations and enhancing mission efficiency and robustness.
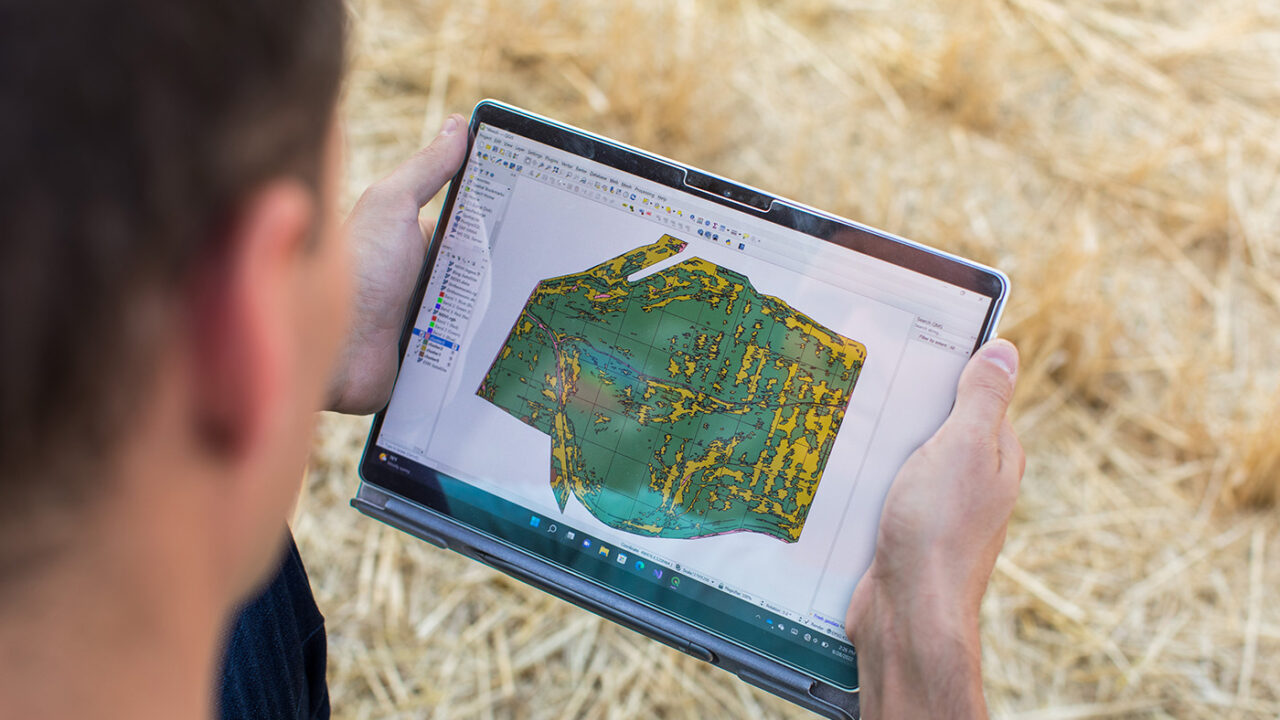
Nowadays, users can create DEMs with just one click, thanks to radar satellites providing continuous, high-precision data on the Earth's surface and increasingly fast and accessible open-source software. This allows for effective monitoring of terrain changes and natural phenomena.
Nemotron-4 340B is an advanced model family for synthetic data generation and AI alignment. Trained on 9 trillion tokens, it excels in optimizing performance and ensuring data quality, significantly enhancing AI capabilities across various industries.
With the significant rise in UAV usage in recent years, concerns about their safety have also increased. In this regard, a new system has been developed that leverages computer vision and deep learning algorithms to accurately and quickly detect and track drones.
AI learnt to decode dog barks, identifying playful versus aggressive barks, as well as the dog’s age, sex, and breed. Originally trained on human speech, AI models have achieved impressive accuracy, offering significant advancements in animal care and communication research.
Much like the invigorating passage of a strong cold front, major changes are afoot in the weather forecasting community. The end game? An entirely new way to forecast weather based on artificial intelligence that can run on a desktop computer.
Researchers from the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory and Google Research have seemingly performed magic with their latest creation: a diffusion model that can alter the material properties of objects in images.
During the Spring Update event OpenAI’s presented GPT-4о – the unique omnimodel that integrates text, audio and image processing, allowing it to work faster and more efficiently than ever before.
SenseTime Group's latest AI model, SenseNova 5.0, has sparked a surge in market interest with its impressive advancements, including enhanced knowledge processing, mathematical reasoning, and linguistic abilities.
Llama 3, Meta AI's latest advancement, boasts unmatched language understanding, enhancing its capacity for complex tasks. With expanded vocabulary and advanced safety features, the model ensures improved performance and versatility.
Explore the forefront of AI music synthesis with Udio and Suno platforms. Music generators enable users to effortlessly generate full-fledged songs across diverse genres while offering customizable features for experimenting with styles and crafting original melodies in seconds.
Мachine "unlearning" allows generative AI to selectively forget problematic data without extensive retraining. This method can ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards while maintaining creative capabilities of image-to-image models.
Google’s DeepMind developed a new method for long-form factuality in large language models, – Search-Augmented Factuality Evaluator (SAFE). The AI fact-checking tool has demonstrated impressive accuracy rates, outperforming human fact-checkers.
MIT researchers have developed a new framework, simplifying image generation into a single step. The team enhanced existing models like Stable Diffusion, by demonstrating the new framework's ability to quickly create high-quality visual content.
Elon Musk's xAI Corp introduces Grok-1, a new LLM equipped with 314 billion parameters and a Mixture-of-Experts architecture. Released as open source under the Apache 2.0 license, Grok-1 is set to catalyze advancements in AI research.
Stability AI presented the latest advancement in image generative AI models – Stable Diffusion 3. Its expanded parameter range and diffusion transformer architecture ensure smooth generation of complex, high-quality images and accurate text-to-visual translation.
OpenAI's latest creation Sora crafts captivating videos, offering unparalleled realism of visual compositions. Leveraging a fusion of language understanding and video generation the model can interpret text prompts, accommodate various input modalities, and simulate dynamic camera motion.
Drawing inspiration from its predecessor Gemini, Gemma is focused on openness and accessibility, offering versatile models suitable for various devices and frameworks. The model marks a significant step towards democratizing AI while emphasizing its responsible development and transparency.
Amazon's latest TTS model with its innovative architecture sets a new benchmark for speech synthesis. BASE TTS not only achieves unparalleled speech naturalness but also demonstrates remarkable adaptability in handling diverse language attributes and nuances.
MPT-7B offers optimized architecture and performance enhancements, including compatibility with the HuggingFace ecosystem. The model was trained on 1 trillion tokens of text and code and sets a new standard for commercially-usable LLMs.
Deep active learning blends conventional neural network training with strategic data sample selection. This innovative approach results in enhanced model performance, efficiency, and accuracy across a wide array of applications.
The integration of high-throughput computational screening and ML algorithms empowers scientists to surpass traditional limitations, enabling dynamic exploration of materials. This combination has led to the discovery of new materials with unique properties.
Coscientist, an advanced AI lab partner, autonomously plans and executes chemistry experiments. Showcasing rapid learning, the system is proficient in chemical reasoning, utilization of technical documents, and adept self-correction.
The StableRep model enhances AI training through the utilization of synthetic imagery. By generating diverse images via text prompts, it not only solves data collection challenges but also provides more efficient and cost-effective training alternatives.
Researchers have joined forces to create a programmable quantum processor that operates with high fault tolerance based on logical qubits. This opens up new prospects for large-scale and reliable quantum computing, capable of solving previously intractable problems.
The Turing test, once groundbreaking for machine thinking, is now limited by AI's ability to mimic human reactions. A new study introduces a three-step system to determine whether artificial intelligence can reason like a human.
QuData introduces an innovative AI-powered breast cancer diagnostic system. This transformative technology ensures early detection and prompt intervention, marking a significant step forward in accessible, accurate, and timely treatment with better outcomes.
A groundbreaking NLP model Gemini AI is set to surpass existing benchmarks. With its multimodal prowess, scalability across various domains, and integration potential within Google's ecosystem, Gemini AI represents a significant leap in AI technology.
ALERTA-Net is a new deep neural network that combines social networks, macroeconomic indicators and search engine data. The unique model predicts stock price movements and stock market volatility, going beyond traditional analysis methods.
In 1950, British scientist Alan Turing proposed a test to determine whether machines can think. To date, no artificial intelligence has yet successfully passed it. Will ChatGPT be the first?
Lincoln Laboratory is actively advancing efforts to diminish the energy consumption of AI models. Their objectives encompass fostering transparency in energy usage and enhancing the efficiency of AI model training.
OpenAI had an impressive DevDay introducing new features. Let's dive into the world of innovation and explore new horizons in the landscape of artificial intelligence. Find out about all the new amazing possibilities in our article!
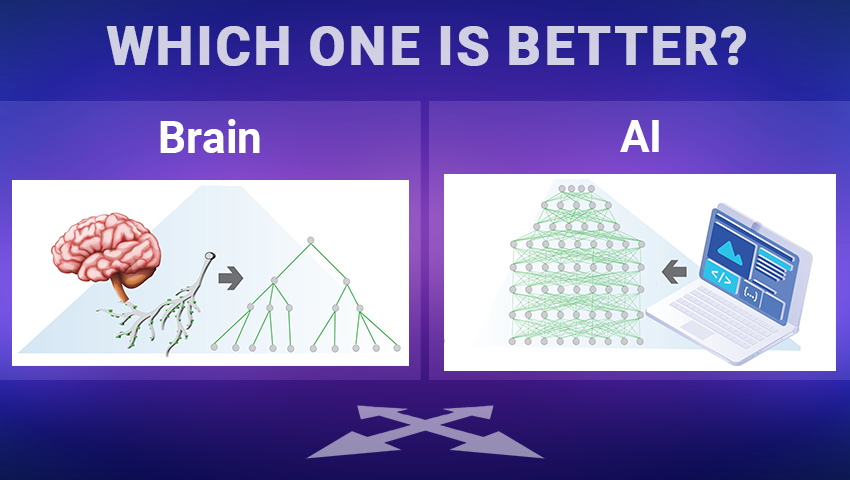
Continuing research on tree-like architectures, scientists from Bar-Ilan University examine the need for deep learning in AI and suggest alternative machine learning methods that may be more effective for complex classification tasks.
Researchers from the Institute for Assured Autonomy highlight new methods for ensuring safety in the growing world of unmanned aircraft systems using advanced artificial intelligence techniques and simulation environments.
The latest motion estimation method can extract long-term motion trajectories for every pixel in a frame, even in the case of fast movements and complex scenes. Learn more about the exciting technology and the future of motion analysis in this article about OmniMotion.
Inspired by ants, researchers from the Universities of Edinburgh and Sheffield are developing an artificial neural network to help robots recognize and remember routes in complex natural environments.
Recent AI research centered around tree-based architectures opens new perspectives for training artificial neural networks.
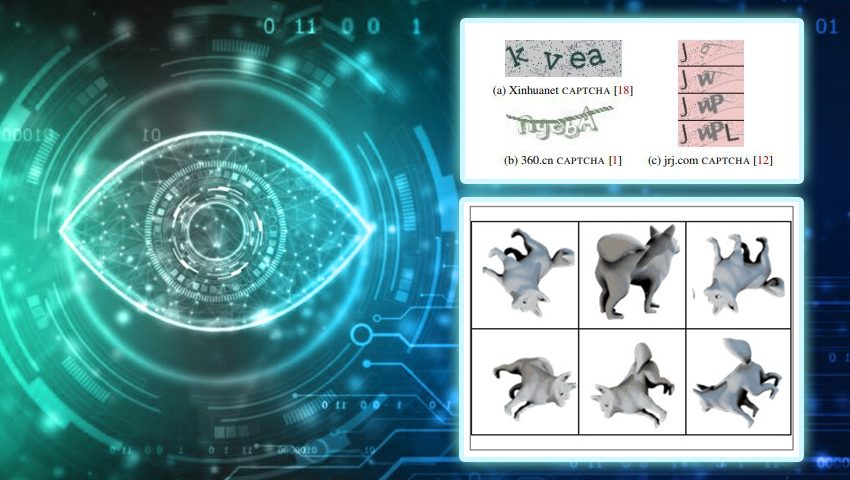
Recent research reveals that despite CAPTCHAs' extensive use as a defense against automation, nowadays bots outperform humans in both speed and accuracy when it comes to solving CAPTCHAs.
SeamlessM4T breaks down language barriers with its comprehensive translation and transcription capabilities, This AI model can easily convert speech or text, enabling real-time translation, and fostering cross-cultural understanding.
The OncoNPC model's predictions offer potential for personalized treatments by pinpointing the source of challenging tumors, facilitating targeted interventions. The computational model can analyze the sequence of about 400 genes to find a previously unseen tumor.
IBM and NASA deploy an open-source geospatial AI model on Hugging Face. They aim to broaden accessibility to NASA satellite data and expedite the pace of climate-related discoveries.
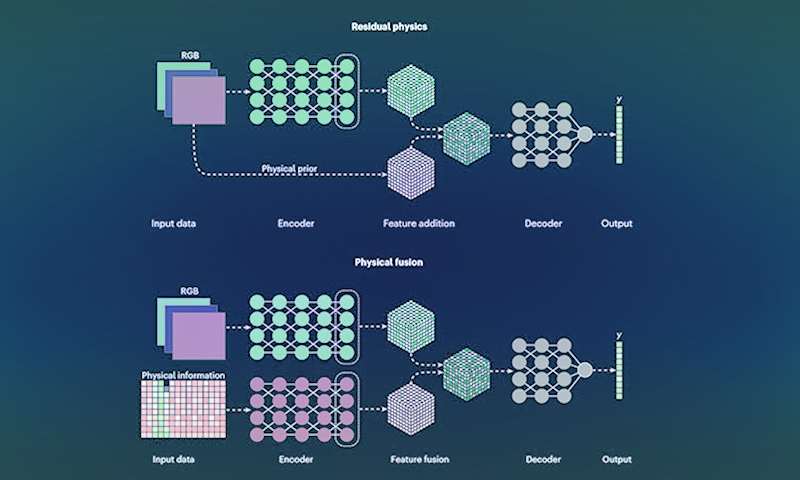
New research focuses on enhancing computer vision technologies by incorporating physics-based awareness into data-driven techniques. This hybrid AI-powered computer vision empowers machinery to intelligently perceive, interact, and respond to real-time environments.
Through the groundbreaking "curious replay" method, AI agents gain the ability to self-reflect and learn from novel experiences, resulting in a substantial enhancement of their adaptability and performance.
A team at Stanford has developed Sophia, a new approach that optimizes pretraining of LLMs. Using the two key techniques, it could help researchers to train LLMs in half the time, thus reducing costs and making it affordable for small organizations and academic groups.
A groundbreaking AI system uses non-invasive methods and fMRI scanner data to translate thoughts into continuous text. With the achieved success rates in converting the content of human thoughts the semantic decoder opens up new possibilities for enhancing communication.
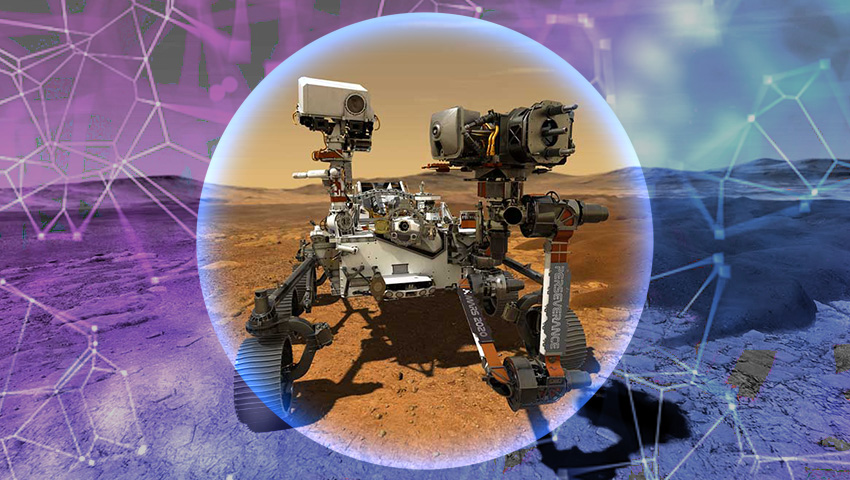
The European Space Agency is developing a sample retrieval system using neural networks, aiming to collect and transport samples from Mars. The challenging mission of returning samples gathered by Perseverance rover is considered crucial for unlocking the mysteries of the Red Planet.
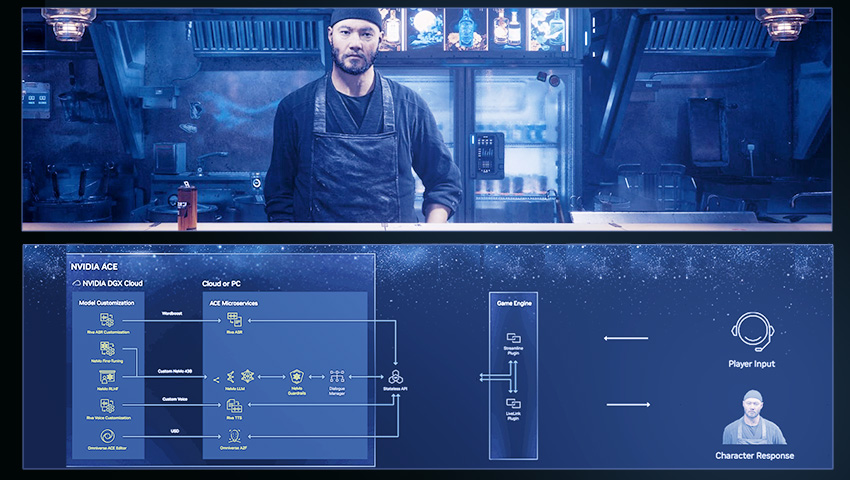
Generative AI is revolutionizing the world of gaming by transforming virtual characters and enhancing their conversational skills. The NVIDIA Avatar Cloud Engine (ACE) for Games empowers developers to infuse intelligence into NPCs, reshaping gaming experiences and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Researchers are working on a more effective way to train machines for uncertain, real-world situations. A new algorithm will decide when a “student” machine should follow its teacher, and when it should learn on its own.
A new architecture aims to overcome the existing limitations of neural networks and symbolic AI. Developed model already demonstrates high effectiveness in solving logical problems and provides a promising framework for integrating different AI paradigms.
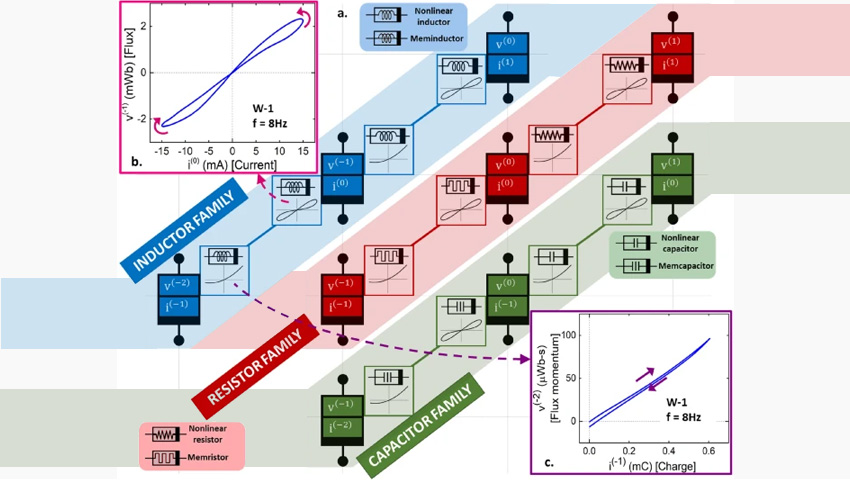
The meminductor joins the previously discovered memristors and memcapacitors in a line of circuit elements that can store and recall previous current or voltage values.
Solar cells based on hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites are a rapidly developing area of alternative energy. These molecules initiated the development of a new class of photovoltaic devices – perovskite solar cells.
The researchers used a diverse set of simple image generation programs to create a dataset for training a computer vision model. This approach can improve the performance of image classification models trained on synthetic data.
Researchers developed a new approach to motion modeling using relative position change. They evaluated the ability of deep neural networks architectures to model motion using motion recognition and prediction tasks.
Researchers designed a new AI algorithm that is designed to visualize data clusters and other macroscopic features in a way that they are as distinct, easy to observe and human-understandable as possible.
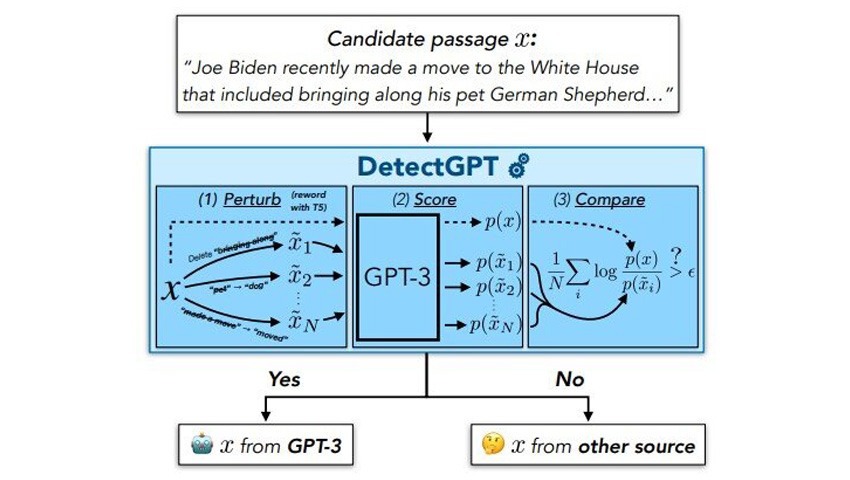
Scholars has developed DetectGPT that can distinguish AI-generated text from human-written text 95% of the time for popular open source LLMs.
Researchers have recently created a new neuromorphic computing system supporting deep belief neural networks (DBNs) - a generative and graphical class of deep learning models.
Scientists have developed the first bio-realistic artificial neuron that can effectively interact with real biological neurons.
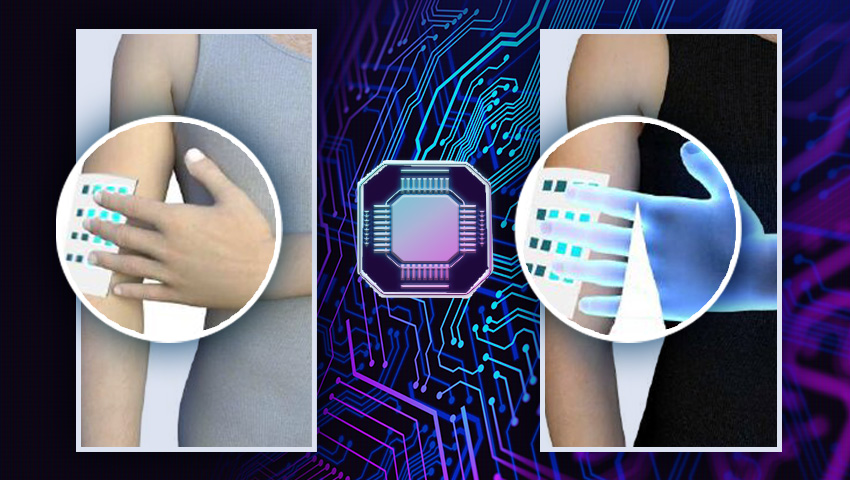
The wireless soft e-skin can both detect and transmit the sense of touch, and form a sensory network, which opens up great possibilities for improving interactive sensory communication.
Meta AI launched LLaMA, a collection of foundation language models that can compete with or even outperform the best existing models such as GPT-3, Chinchilla and PaLM.
MusicLM is a new music generation AI that creates high-quality music based on textual descriptions in a similar way that DALL-E generates images from texts.
Scientists from the University of Michigan conducted a study of robot behavior strategies to restore trust between a bot and a human. Can such strategies fully restore trust and how effective are they after repeated errors?
A group of researchers have created a Bayesian machine, an AI approach that performs computations based on Bayes' theorem, using memristors. It is significantly more energy-efficient than existing hardware solutions, and could be used for safety-critical applications.
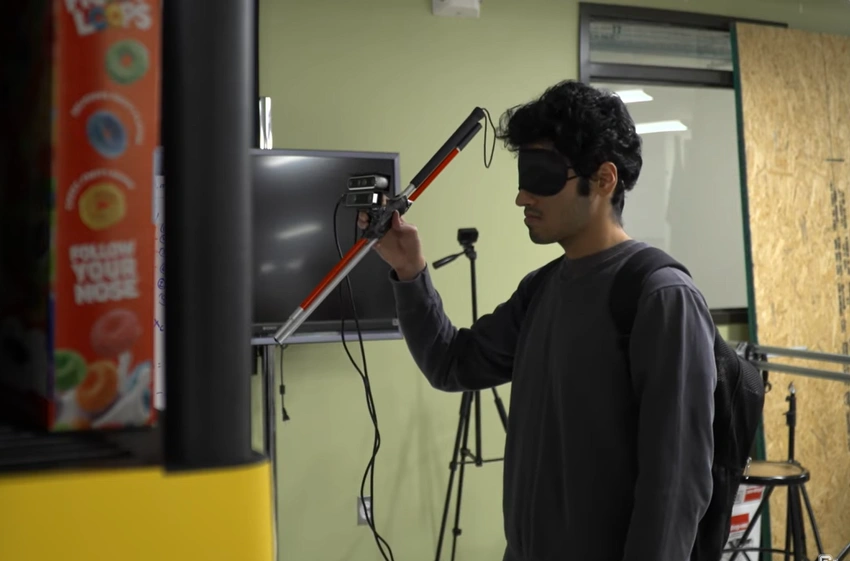
Using advances in artificial intelligence engineers at the University of Colorado Boulder are working on a new type of walking cane for blind or visually impaired.
Text-to-speech models usually require significantly longer training samples, while VALL-E creates a much more natural-sounding synthetic voice from just a few seconds.
Researchers from Stanford University developed a new type of stretchable biocompatible material that gets sprayed on the back of the hand and can recognize its movements.
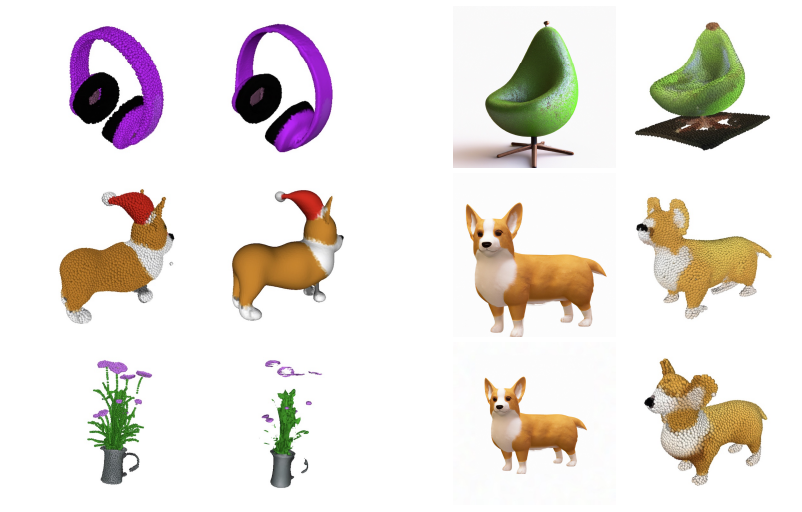
Point·E is a new system for text-conditional synthesis of 3D point clouds that first generates synthetic views and then generates colored point clouds conditioned on these views.
Self-driving cars have long been considered the next generation mode of transportation. To enable autonomous navigation of such vehicles numerous different technologies need to be implemented.
New research from the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory uses machine learning, data analysis and artificial intelligence to identify potential nuclear threats.
Researchers have discovered new ways for retailers to use AI in conjunction with in-store cameras to better understand consumer behavior and adapt store layouts to maximize sales.
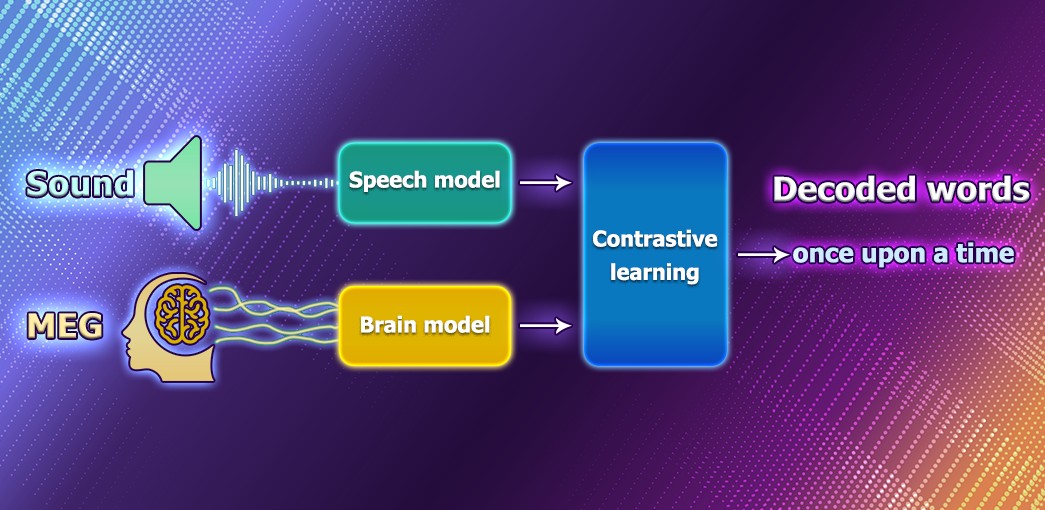
Decoding speech based on brain activity has been a long-established goal of neuroscientists and clinicians. Nowdays, Meta is working on an AI model that can decode speech from noninvasive recordings of brain activity to help people after traumatic brain injury.
Look to Speak is designed to help those with motor function impairments and speech difficulties to communicate more easily. The app lets people use their eyes to select pre-written phrases and have them spoken out loud.
By 2050 humanity will have to almost double the global food supply to make sure that every dweller of the planet has enough food. With climate change going at increasing speed, water resources drop and arable lands erode, doing that sustainably will be a huge challenge for us.
During the last decade, one of the biggest issues in the gaming industry is the explosive growth of the AAA video games production cost. Studios are always on the look-up for technologies that could help bring down the cost of game development. Recent advances in the neural image generation models bring some hope that the realization of this dream may be not so far away.
A group of scientists using machine learning "rediscovered" the law of universal gravitation.
A group of scientists using machine learning "rediscovered" the law of universal gravitation.
Ukraine started using Clearview AI facial recognition software to identify dead Russian soldiers and Ukrainian people who were killed in the conflict. Hoan Ton-That, the company's chief executive, told Reuters that Ukraine's defense ministry began using the software in March this year.
The Nature Conservancy reconsidered its marketing strategy via digital transformation with the help of SAS Customer Intelligence 360. As a result this international environmental nonprofit had its best year ever for membership revenue. That as nothing else contributes to advancing its mission of creating a more sustainable future.
“We find that DALL·E also allows for control over the viewpoint of a scene and the 3D style in which a scene is rendered” OpenAI explains. Produced images can range from illustrations to objects, and also adjusted real-world pictures.
“Employers and employees alike need to change their perspective. The future of work is already here and the introduction of technology does not affect work in a uniform way. We must acknowledge where it supplements existing work and invest in a targeted reskilling approach that recognises the new roles technology is creating and ensures human and machine labour complement one another.
AI-powered engines review and analyze information in the knowledgebase, deal with model deployment, and check the performance. They introduce a new approach in which apps can take advantage of artificial intelligence to enhance operational effectiveness and help to address different business challenges.
“Over the last decade, Affectiva has continuously pursued new patents as we have pioneered and advanced the fields of Emotion AI and Human Perception AI. The breadth and depth of our patent portfolio reflect our commitment to pushing the boundaries of computer vision, machine learning, deep learning and AI at the edge; and, is a testament to our leadership in defining the many creative and diverse applications of Human Perception AI that are shaping industries today and in the future.”
With increased social media usage in recent years, and all of us living our lives online yet more, we need to develop the ways to reduce threats, ensure our safety and remove interactions that are creating concern. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a progressed machine learning technology that plays an important role in contemporary life and is also essential in how today's social media networks function.
The abilities that computer systems have are very advanced. The earliest equipment not only helped people solve complex mathematical problems, but also stored large amounts of information. Today computers operate complex equipment and systems to prevent human errors.